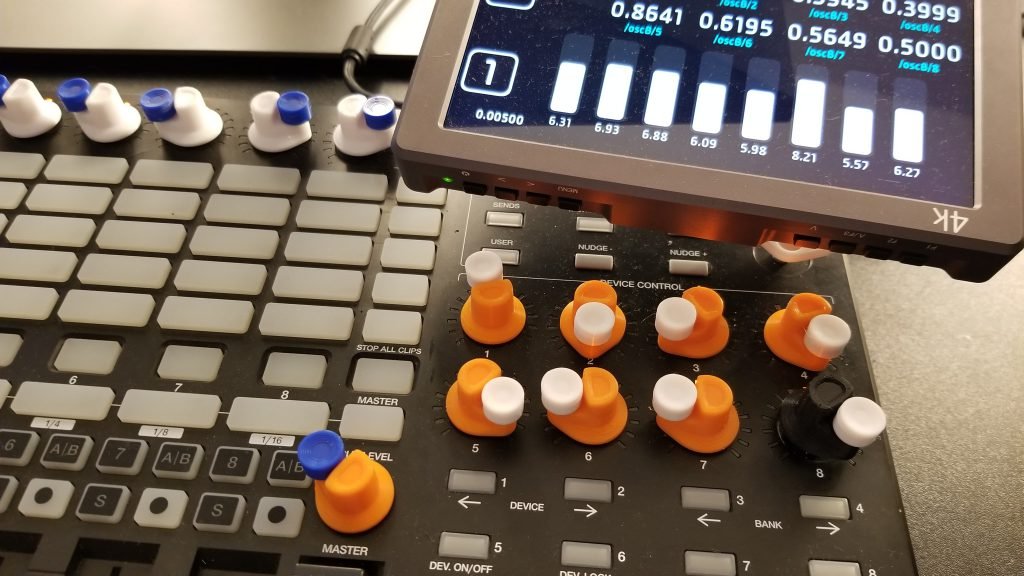
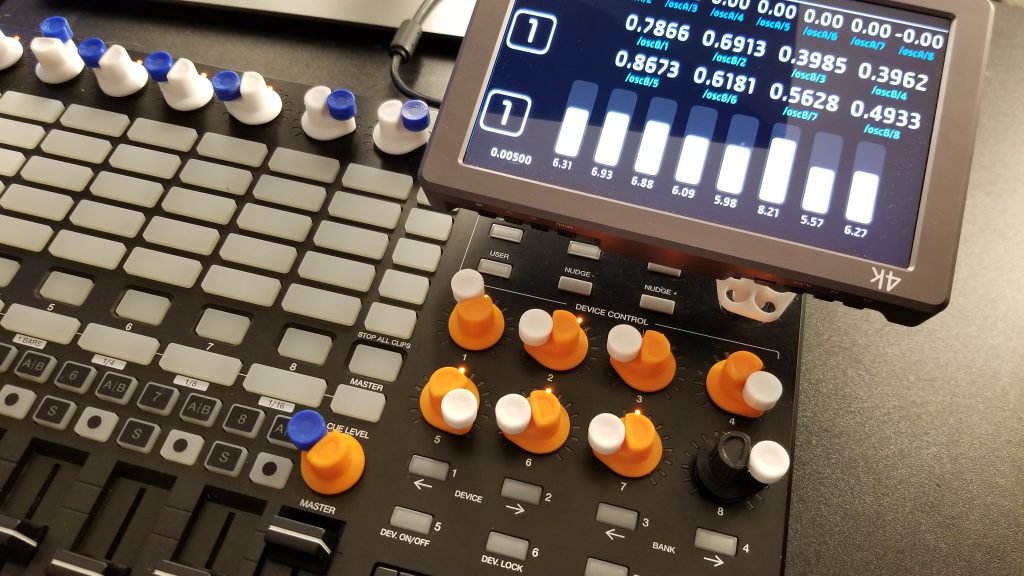
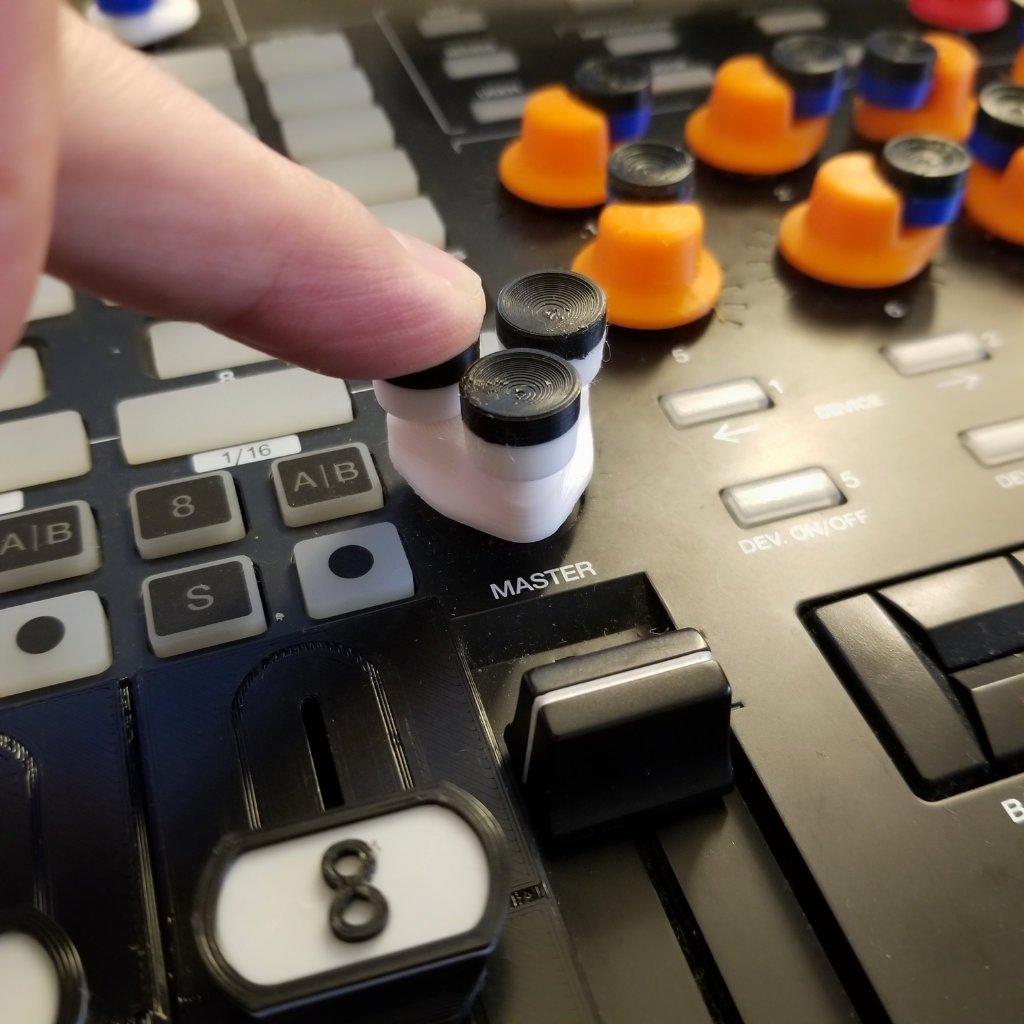
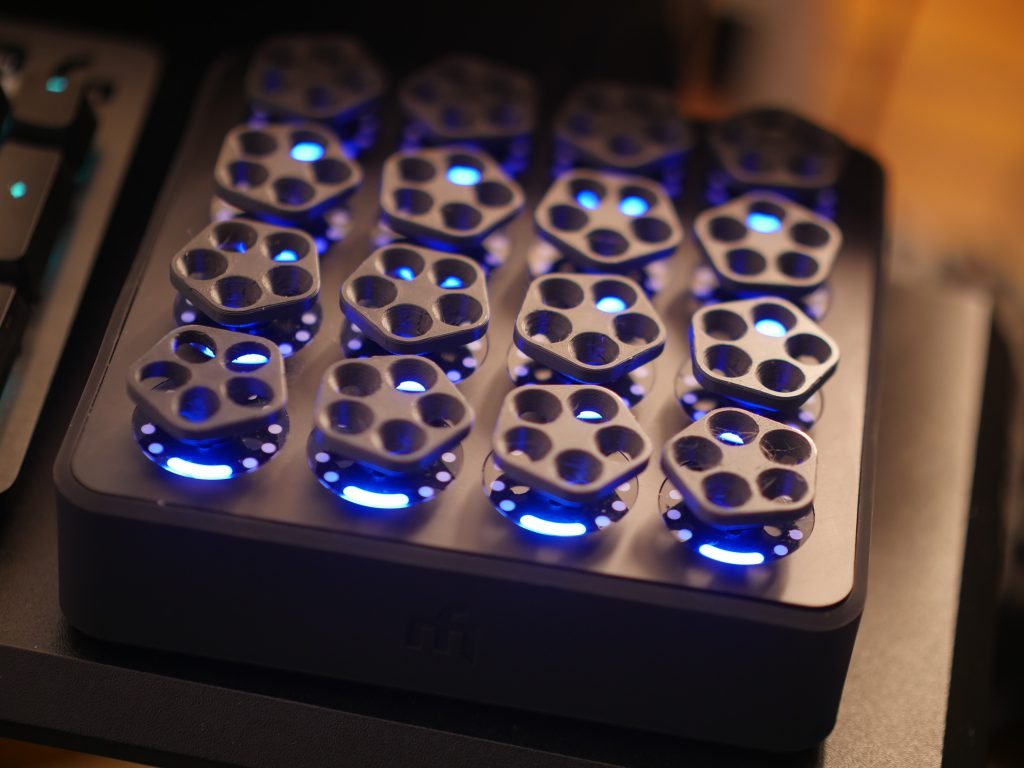
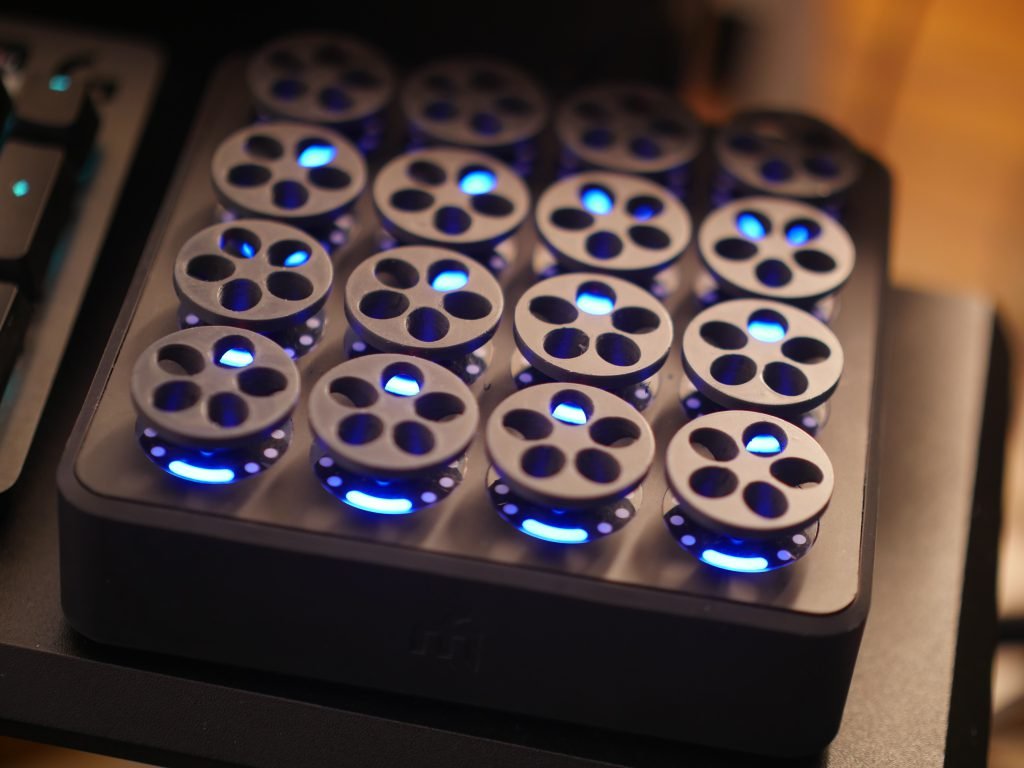
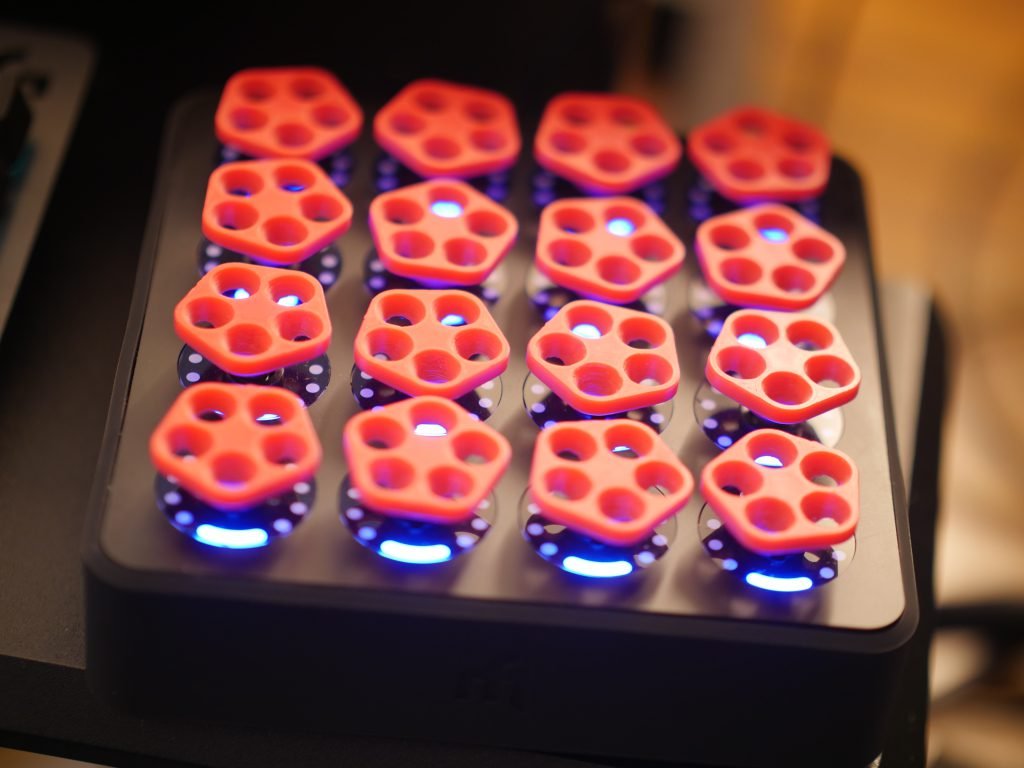
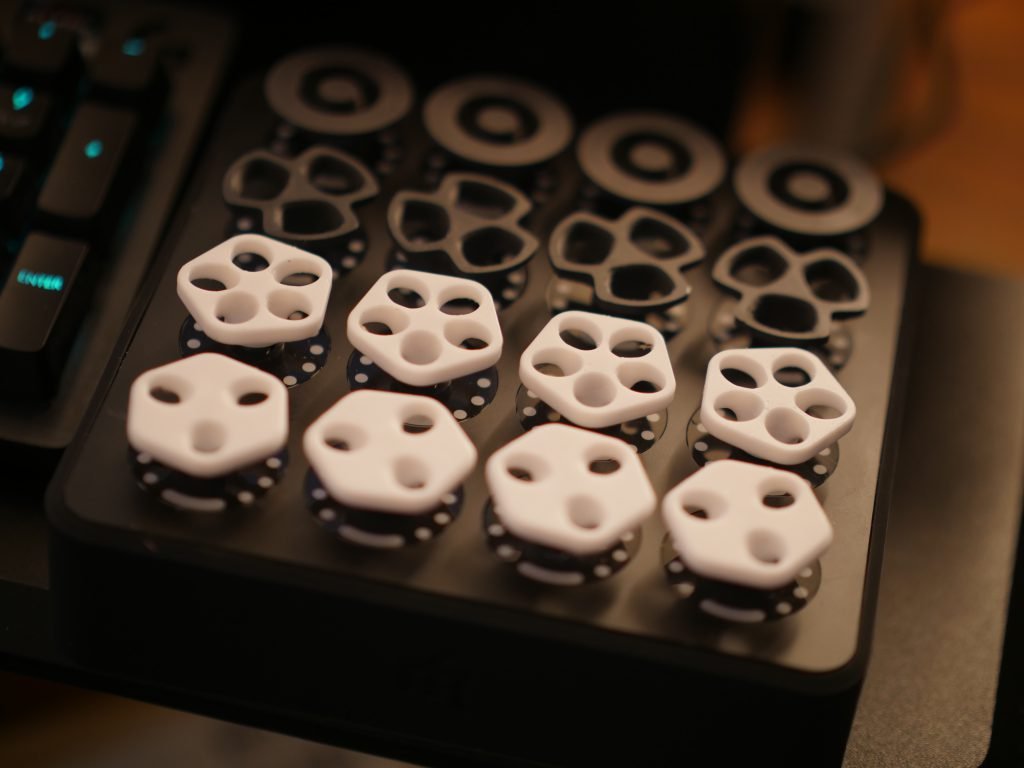
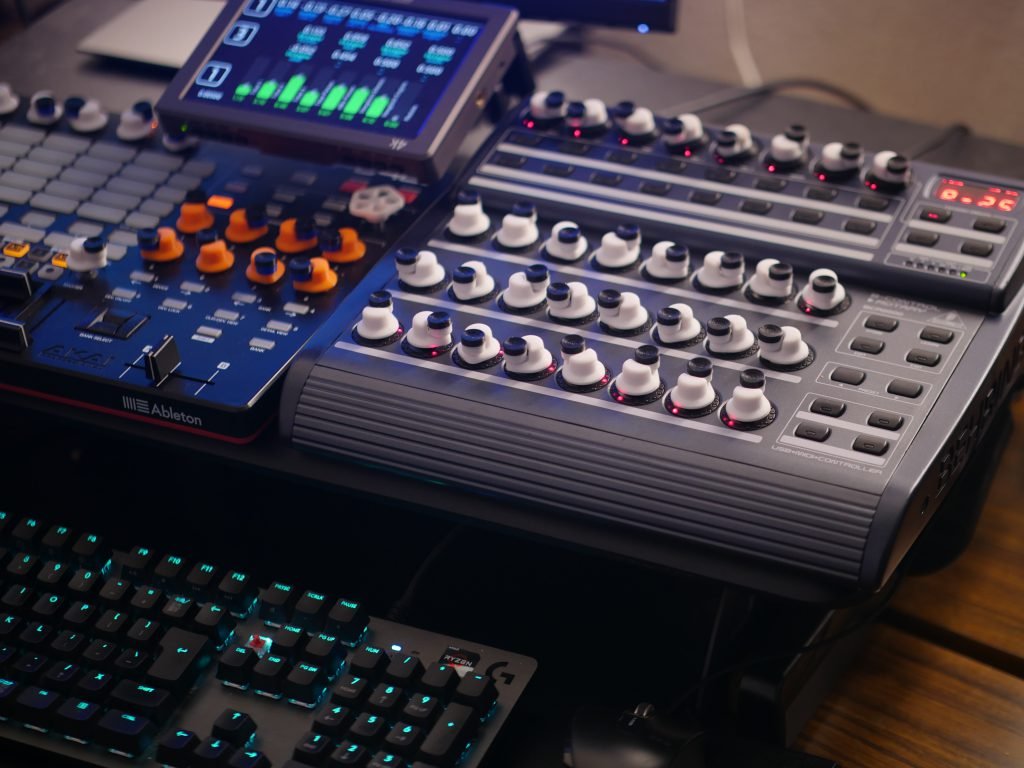
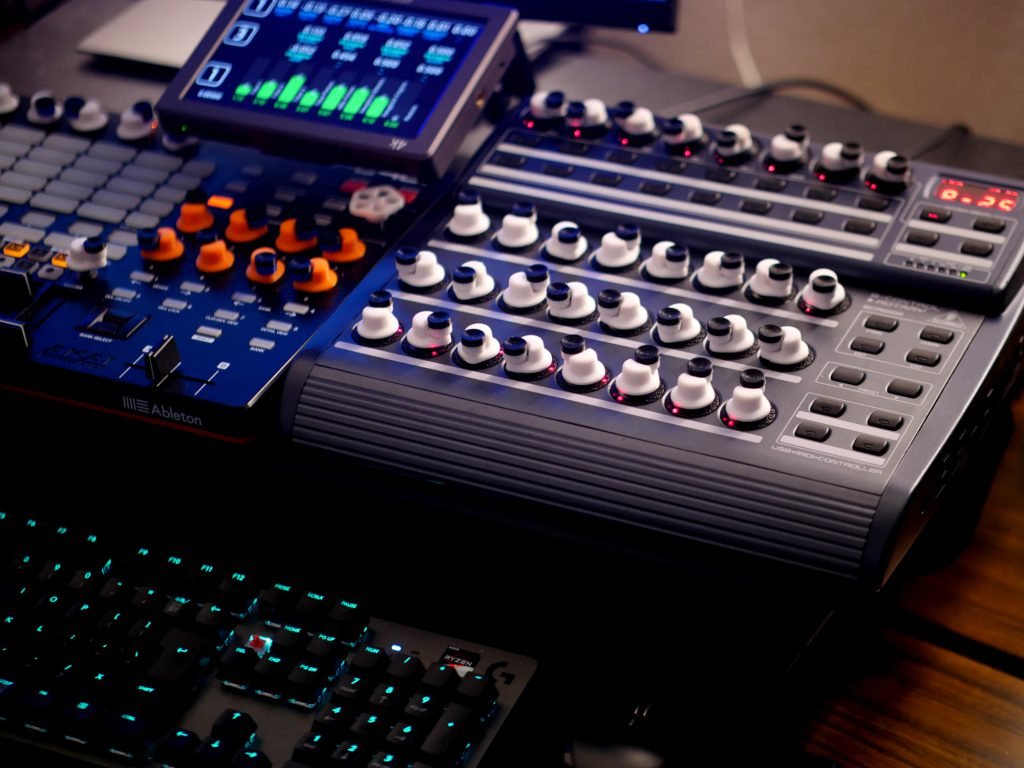
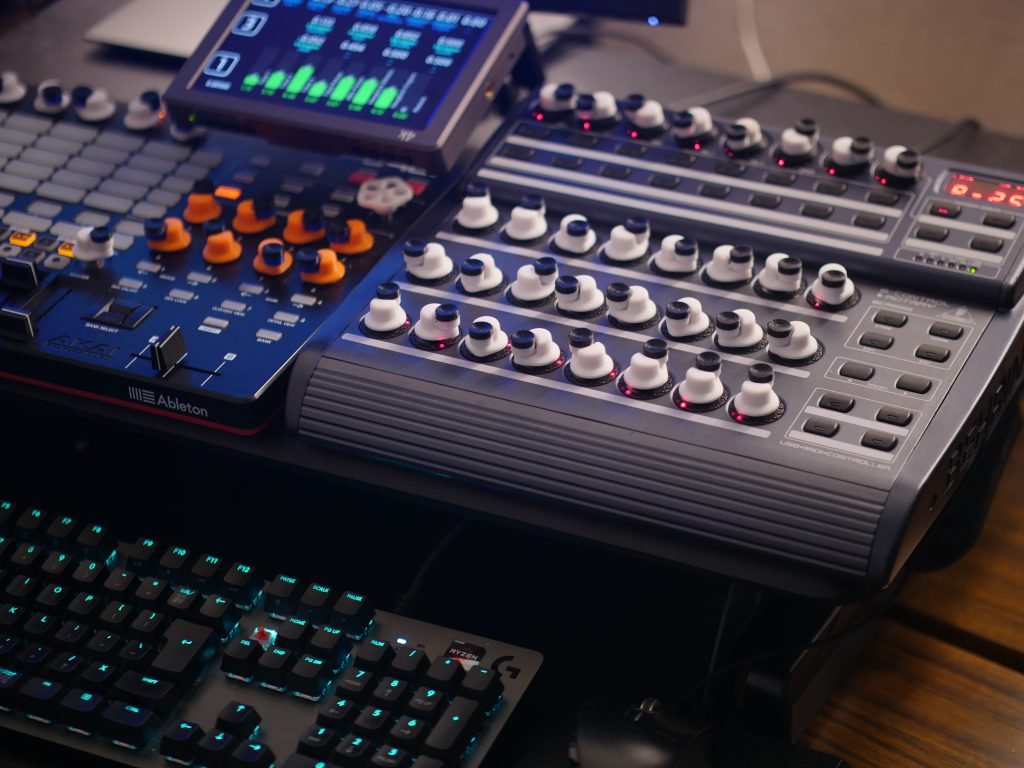
Introduction
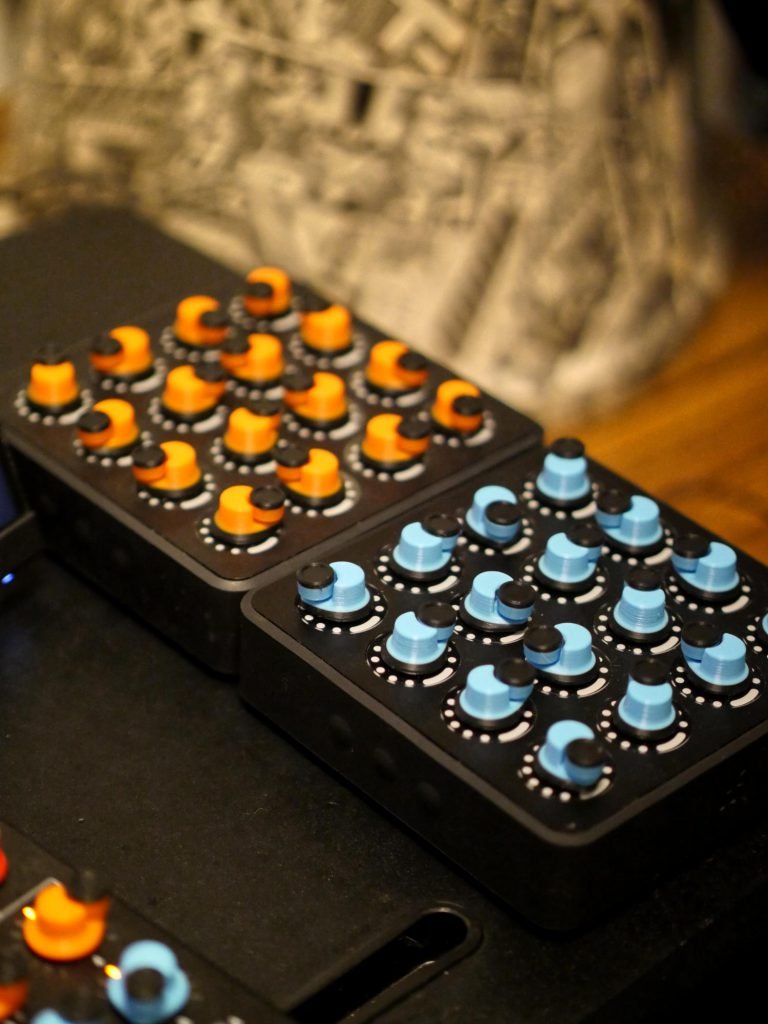
- Purpose of miniature jog wheels for software control
- Advantage of endless rotation for numerical input
- Context of fingertip control versus traditional knobs
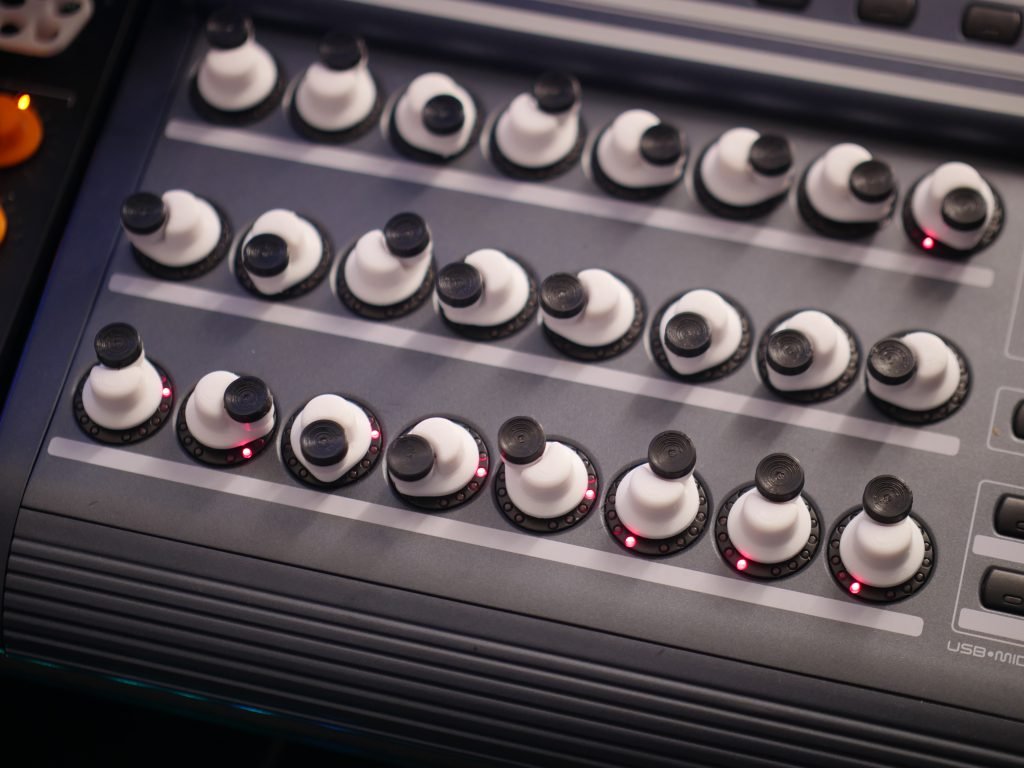
Physical Design Considerations
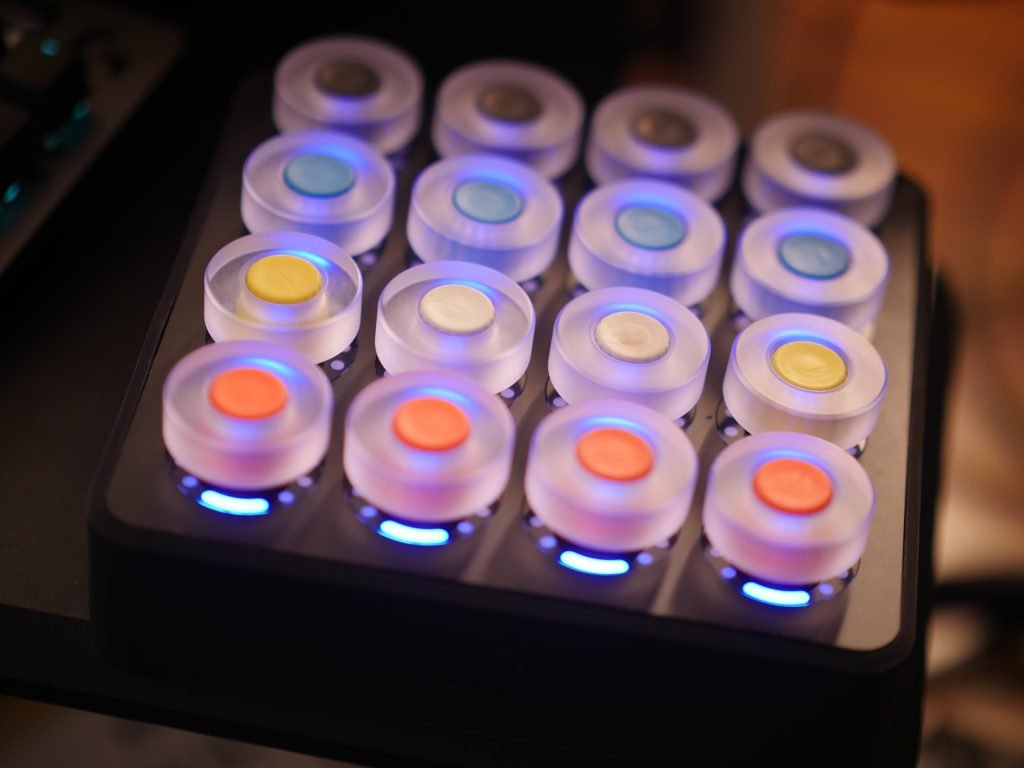
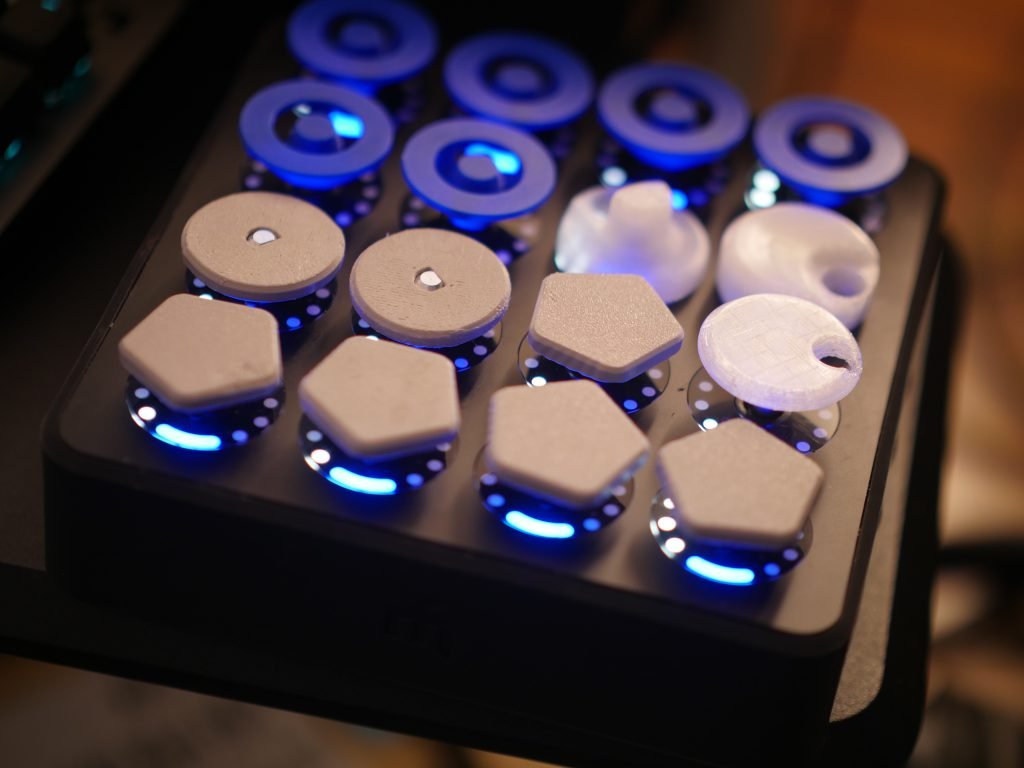
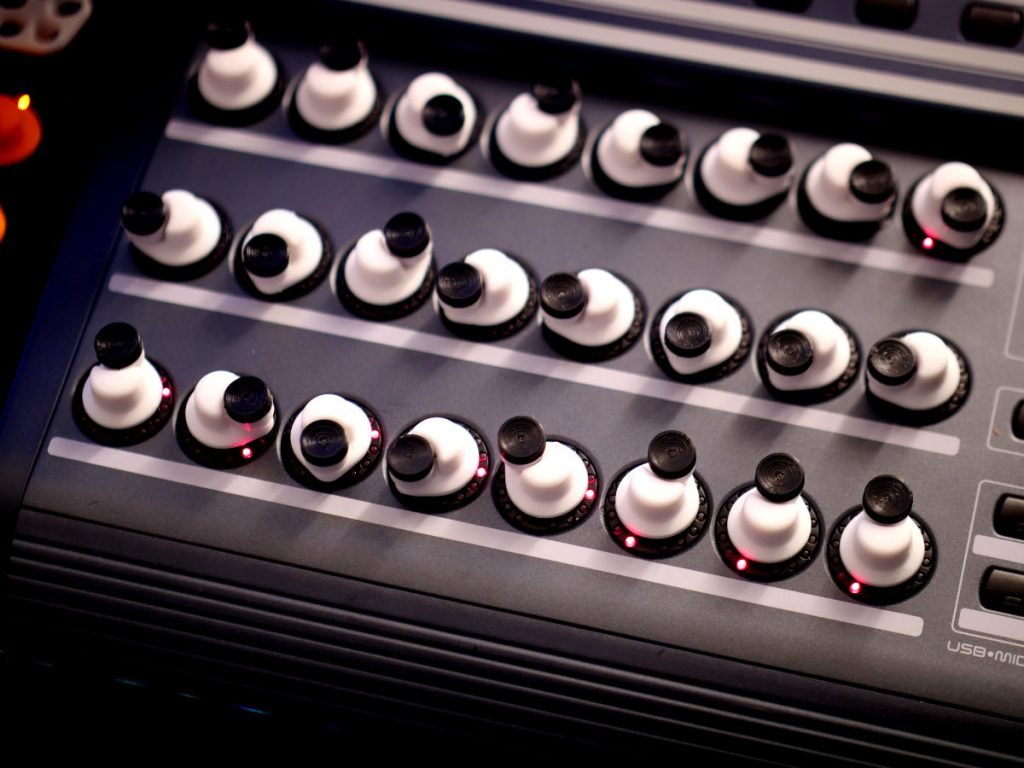
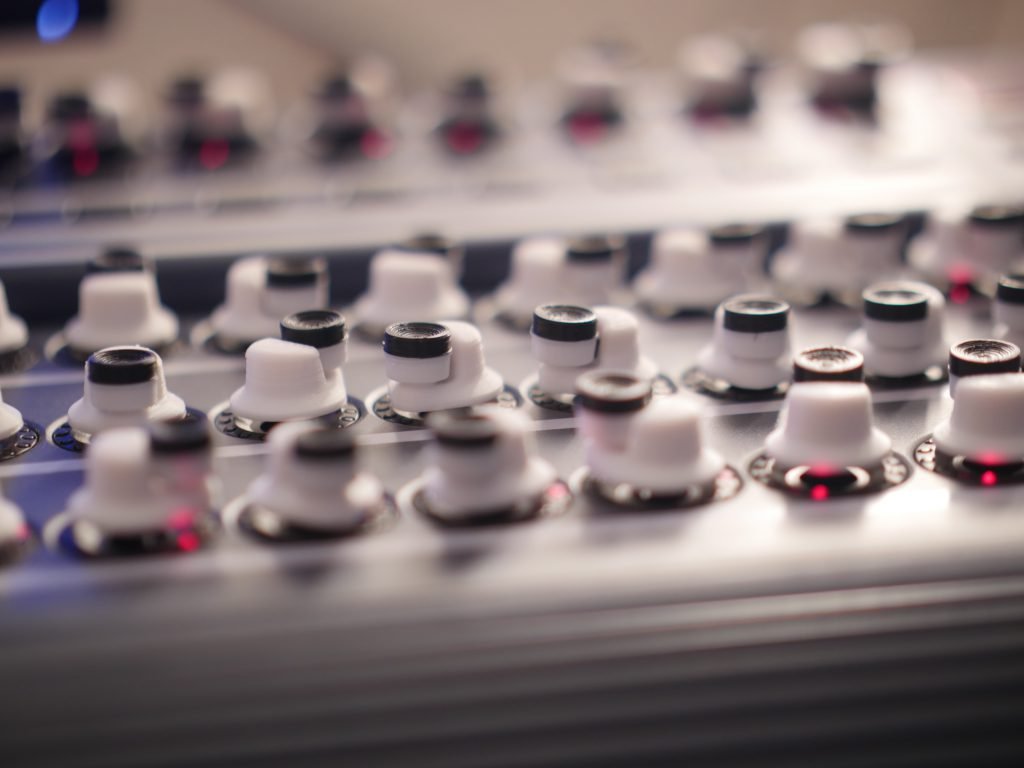
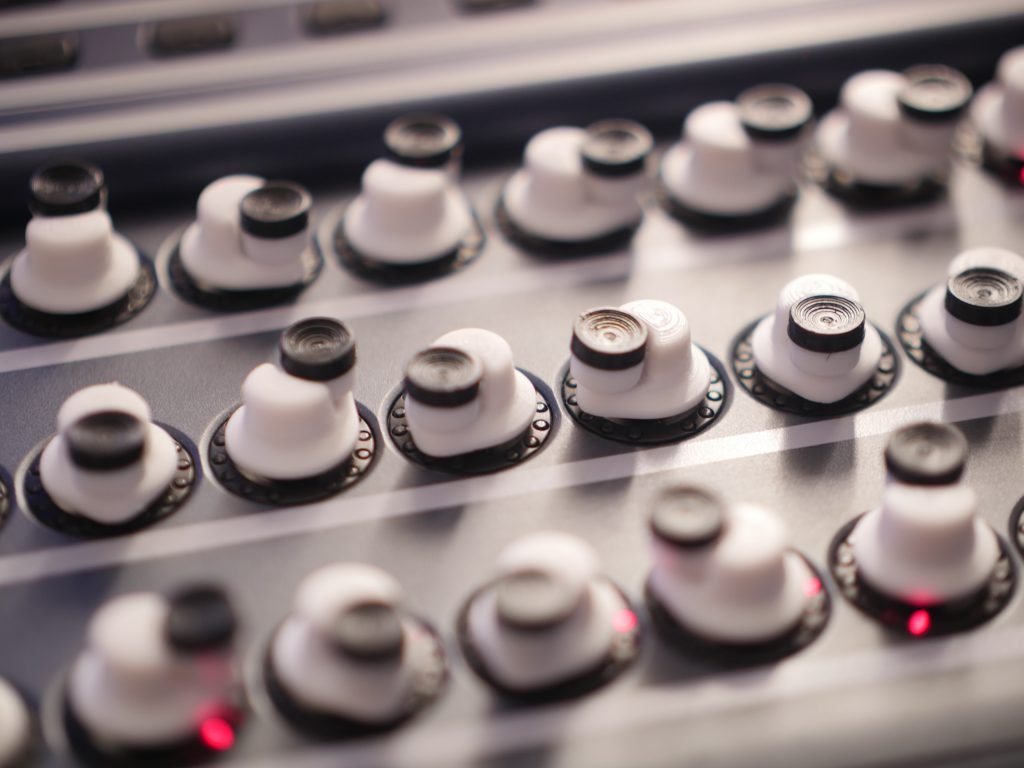
- Optimal diameter for fingertip manipulation
- Surface texture and grip patterns
- Height and profile for comfortable access
- Material selection for durability and feel
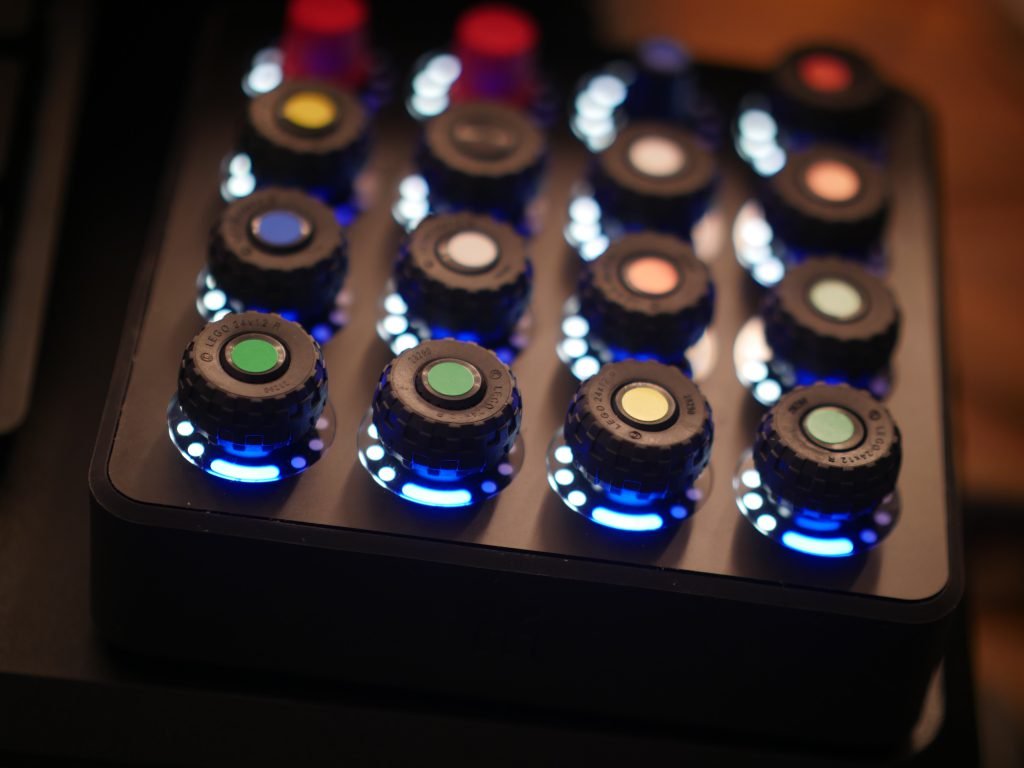
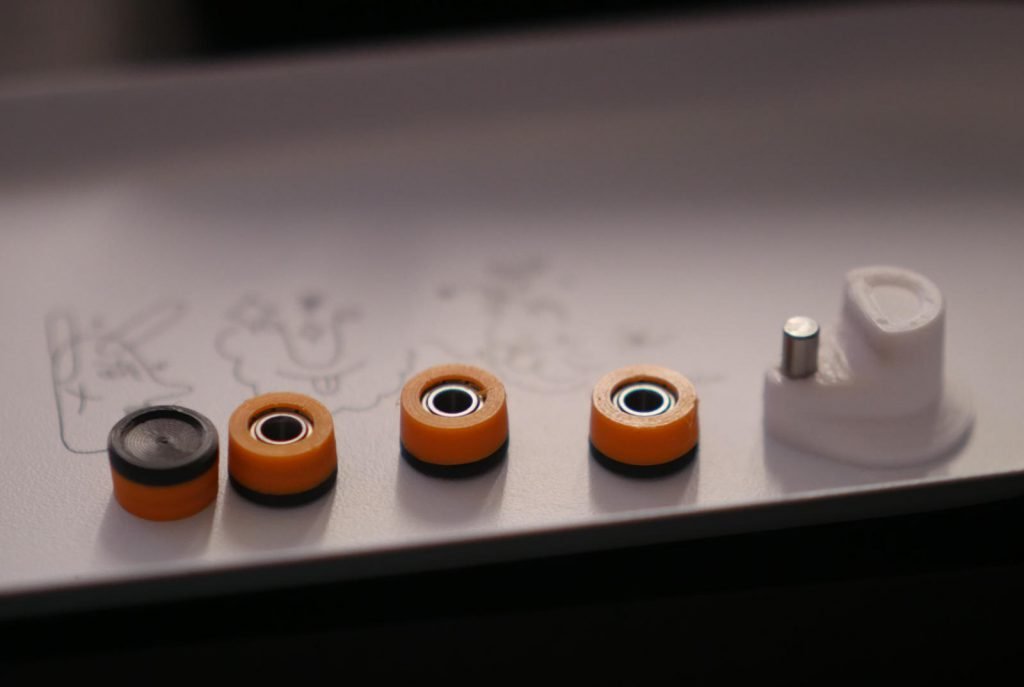
Mechanical Implementation
- Rotary encoder selection and specifications
- Bearing integration for smooth operation
- Mounting solutions to prevent wobble
- Assembly method for DIY creators
Control Characteristics
- Fine movement detection for precise adjustments
- Acceleration curves for varied rotation speeds
- Implementing detents vs smooth rotation
- Relationship between physical movement and software input
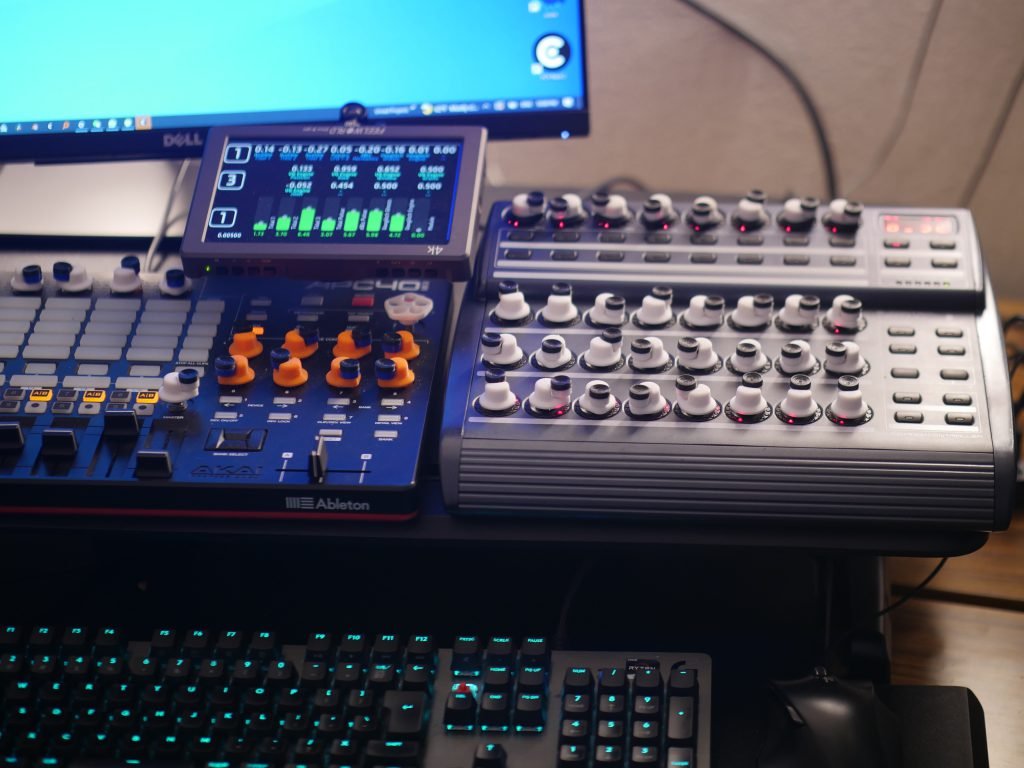
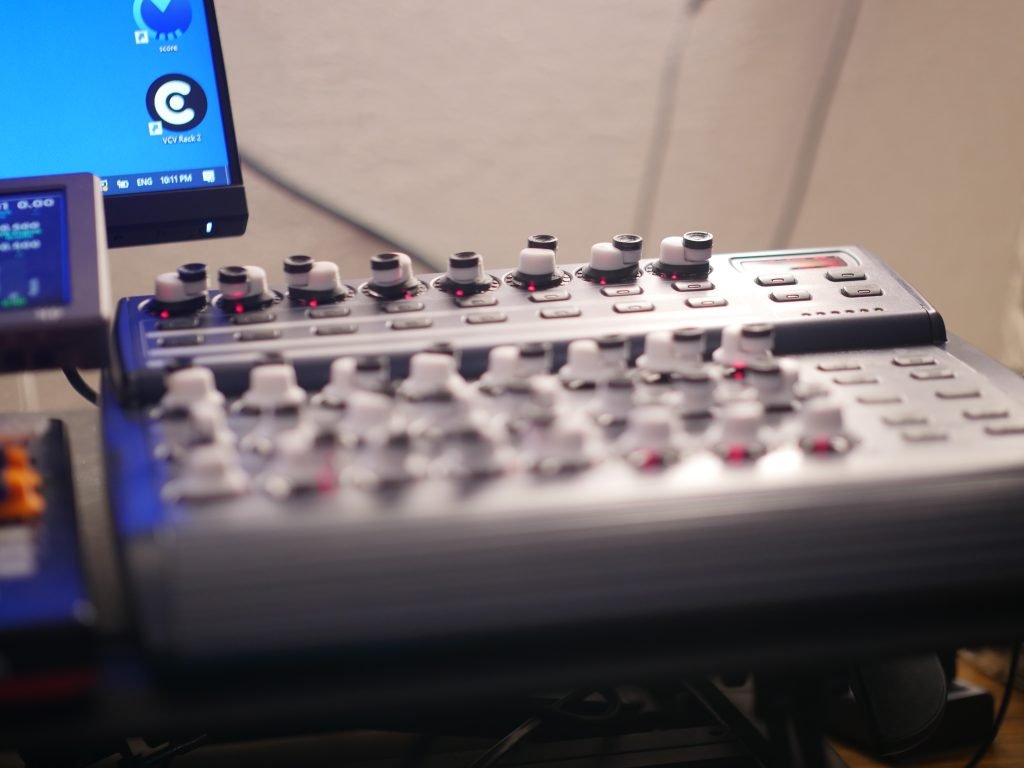
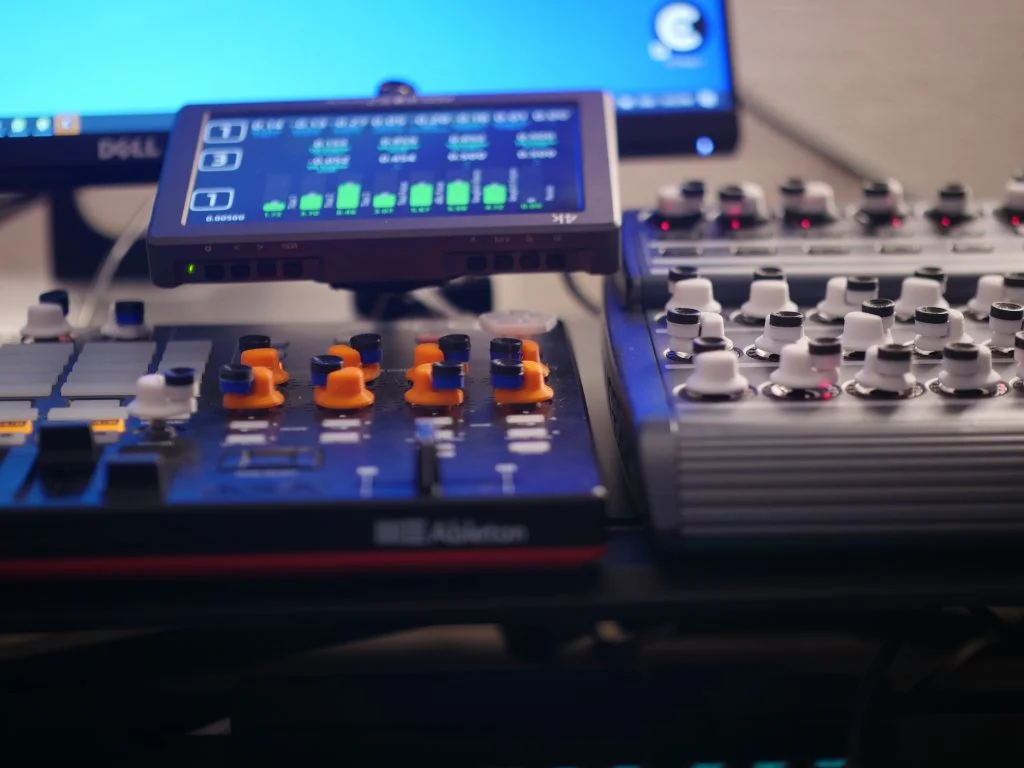
Software Integration
- Protocol selection (USB HID, MIDI, custom)
- Driver considerations
- Acceleration curve implementation
- Example applications and use cases
Build Documentation
- Parts list and sourcing
- Step-by-step assembly process
- Common issues and solutions
- Testing and calibration